For March, it鈥檚 a renal three-fer: sodium, potassium and chlorine
Every month in 2019 we are looking at one or more chemical elements essential for life in commemoration of the 150th anniversary of Mendeleev’s periodic table. For January and February, we selected hydrogen and iron, respectively, and described their function in biochemical reactions involving electron transport.
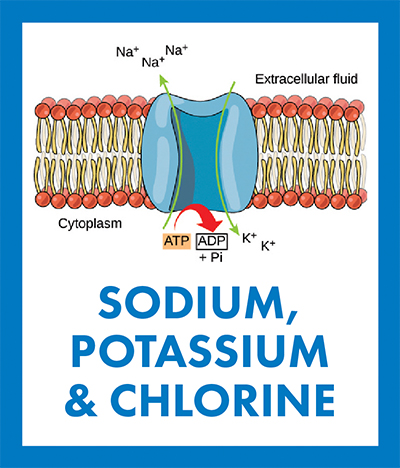 The Na+/K+ pump uses energy from the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate into adenosine diphosphate and inorganic phosphate to move 3 Na ions out to the extracellular space and 2 K ions into the cytoplasm, creating a charge imbalance across the cellular membrane. CNX OpenStax/Wikimedia Commons
The Na+/K+ pump uses energy from the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate into adenosine diphosphate and inorganic phosphate to move 3 Na ions out to the extracellular space and 2 K ions into the cytoplasm, creating a charge imbalance across the cellular membrane. CNX OpenStax/Wikimedia Commons
March is , so we are highlighting three elements central to renal function: sodium, or Na; potassium, or K; and chlorine, or Cl.
Sodium and potassium, atomic numbers 11 and 19, respectively, are highly reactive metals with similar chemical properties, both listed in group 1, the alkali metals, of the periodic table. Both have a single valence electron in their outer shell, which they readily donate, creating positive ions, or Na+ and K+ cations. Chlorine, a gas at room temperature with atomic number 17, is a highly reactive element with an affinity for electrons. As a strong oxidizing agent, chlorine is abundant as chloride anions, or Cl-, that combine with Na+, K+ and other cations to form chloride salts.
Sodium is the seventh most abundant element on Earth, and potassium is the 17th. They exist in rock-forming minerals such as salt and granite. Chlorine is the 21st most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, occurring exclusively as ionic chloride compounds. Sodium and chlorine, constantly leached by water from mineral salts, are the most abundant elements dissolved in the oceans.
Sodium and potassium ions are crucial for most cells. Microorganisms use transmembrane ion pumps, such as the Na+/H+ antiporter or Na+ translocation systems coupled to metabolic reactions, to move Na+ ions against their concentration gradient, generating electrochemical energy to drive solute transport or to move flagellar motors (in bacteria) and to produce reducing power for biochemical reactions. K+ is the main monovalent cation in prokaryotes; it is essential to maintain intracellular pH, to generate energy via electrochemical gradients and to sustain turgor pressure.
In animals, the Na+/K+ ion pump pushes sodium and potassium across the cell membrane in opposite directions, maintaining a low Na+ concentration and a high K+ concentration inside the cell. This ionic imbalance between the cytosol and the extracellular medium creates a transmembrane potential — or voltage difference — essential to conducting electrical signals in excitable neurons and myocytes. A similar ion transporter moves H+ and K+ ions across the membrane of parietal cells, helping mammals acidify stomach contents and digest food.
Chloride ions are also necessary for all known life. Some prokaryotes use chloride compounds as a carbon and energy source and chlorine ions as terminal electron acceptors during anaerobic growth. In most cells at rest, the concentration of Cl- is lower in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid via activity of gated ion channels that contribute to the polarization of cellular membranes. In animals, parietal cells in the stomach secrete Cl- ions to produce hydrochloric acid required for food breakdown. In humans, the defective protein in the disease cystic fibrosis is an ion channel specific for Cl- whose impaired activity results in less bactericidal activity — and more infections — in the lungs.
A year of (bio)chemical elements
Read the whole series:
For January, it’s atomic No. 1
For February, it’s iron — atomic No. 26
For March, it’s a renal three-fer: sodium, potassium and chlorine
For April, it’s copper — atomic No. 29
For May, it’s in your bones: calcium and phosphorus
For June and July, it’s atomic Nos. 6 and 7
Breathe deep — for August, it’s oxygen
Manganese seldom travels alone
For October, magnesium helps the leaves stay green
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we鈥檒l send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Neurobiology of stress and substance use
MOSAIC scholar and proud Latino, Bryan Cruz of Scripps Research Institute studies the neurochemical origins of PTSD-related alcohol use using a multidisciplinary approach.

Pesticide disrupts neuronal potentiation
New research reveals how deltamethrin may disrupt brain development by altering the protein cargo of brain-derived extracellular vesicles. Read more about this recent 偷拍偷窥 & Cellular Proteomics article.

A look into the rice glycoproteome
Researchers mapped posttranslational modifications in Oryza sativa, revealing hundreds of alterations tied to key plant processes. Read more about this recent 偷拍偷窥 & Cellular Proteomics paper.

Proteomic variation in heart tissues
By tracking protein changes in stem cell鈥揹erived heart cells, researchers from Cedars-Sinai uncovered surprising diversity 鈥� including a potential new cell type 鈥� that could reshape how we study and treat heart disease.

Parsing plant pigment pathways
Erich Grotewold of Michigan State University, an ASBMB Breakthroughs speaker, discusses his work on the genetic regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis.

Calcium channel linked to cancer drug resistance
Researchers discover a protein associated with carboplatin-resistant retinoblastoma, suggesting this protein could be a promising therapeutic target. Read more about this recent Journal of Biological Chemistry paper.

